Flight Management Computer (FMC)
Flight Management Computer (FMC)
Description
The flight management computer (FMC) is one of the main components of the flight management system (FMS). It collects various data about aircraft position and performance, fuel consumption, weather, wind, etc. and performs calculations which influence the flight path. Thus it helps with the facilitation of safe and efficient flight operations. Examples of the tasks performed by the FMC include:
- Navigation and route planning. The FMC calculates the optimal flight route considering various factors such as airways and airspace restrictions.
- Auto flight control. The FMC is linked to the autopilot, enabling automated control of the aircraft's altitude, heading, and speed according to the flight plan.
- Performance optimization. The FMC continuously monitors various aircraft performance parameters (e.g. fuel consumption, engine efficiency, weight, etc.) and optimizes the flight profile for fuel efficiency and operational effectiveness.
- Fuel management. The FMC calculates the most fuel-efficient speeds, altitudes, and vertical profiles.
- Navigation database management. The FMC maintains an extensive database of navigation information (e.g. airports, runways, airways, waypoints, etc.). The data is regularly updated and is used during the calculations.
- Integration with avionics systems. The FMC integrates with various avionics systems, such as the [[Inertial Navigation System (INS)]] and Global Navigation Satellite Sysyem (GNSS), to gather real-time position data.
- Flight monitoring and alerts. The FMC continuously monitors the aircraft's progress, providing alerts and warnings to the flight crew in case of deviations from the planned route, weather-related issues, or any other anomalies.
- Approach and landing guidance. During the descent and approach phases, the FMC assists in providing guidance for instrument approaches.
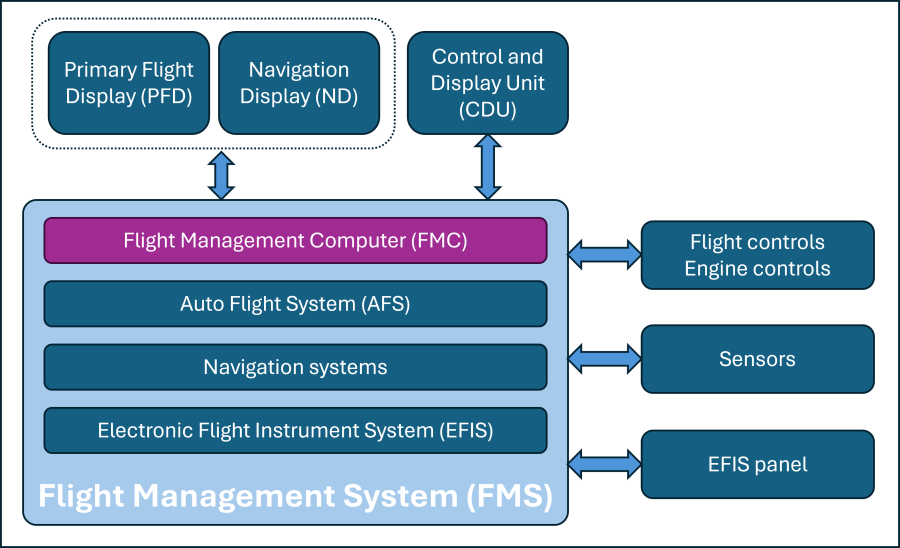
The picture below shows the interactions between the FMC and various other aircraft systems.
Categories